1.Java Web 模块结构
JSP文件和AXPX文件类似,路径和URL一一对应,都会被动态编译为单独class。Java Web和ASP.NET的核心是分别是Servlet和IHttpHandler接口,因此无论是基础的Page文件(JSP、ASPX)方式还是后来发展的MVC方式(Spring MVC、ASP.NET MVC)都是基于核心接口的基础上再次封装和扩展(DispatcherServlet、MvcHandler)。
除JSP文件外,其他全部文件部署在应用目录的WEB-INF子目录下,WEB-INF目录可以认为是ASP.NET中将web.config文件、bin目录和App_开头的运行时目录存放在了一个统一的根目录中。
Java Web的配置文件web.xml也存放在WEB-INF目录下,而ASP.NET的配置文件web.config一般直接存放在应用目录下(ASP.NET其他目录同样可以有web.config文件)。ASP.NET将所有的引用和代码生成的dll都部署在bin中,而Java Web的引用jar和生成的class分别存放在WEB-INF的子目录lib和classes中(参考1)。
综上,类似ASP.NET中的web.config、bin、App_Data等,Java Web中的WEB-INF、web.xml、lib和classes是我们必须了解和掌握的。
|--Assembly Root
|---WEB-INF/
|--web.xml
|--lib/
|--classes/
- WEB-INF目录:Java Web文件的根目录。
- web.xml文件:配置文件(asp.net web.config)。
- lib目录:存放类库文件(asp.net bin)。
- classes目录:存放class文件(asp.net bin)。
2.Java Web项目的基本结构[Eclipse Dynamic Web Project]
Eclipse Dynamic Web Project项目
(1)可以配置需要编译的源码目录和输出目录,默认编译src目录下的源文件到build\classes目录下。
(2)可以配置WEB-INF的根目录,默认为WebContent。
(3)可以选择是否生成默认web.xml文件。
我们创建一个命名为DynamicWP的默认生成web.xml的Dynamic Web Proejct项目。文件结构如下:
|--DynamicWP
|--.settings/
|--build/
|--classes/
|--src/
|--WebContent/
|--META-INF/
|--MANIFEST.MF
|--WEB-INF/
|--web.xml
|--lib/
在Eclipse的项目资源管理器中DyanmicWP项目的视图如下:
|--DynamicWP
|--Deployment Desciptor
|--JAX-WS Web Services
|--Java Resources
|--JavaScript Resources
|--build
|--WebContent
|--META-INF/
|--MANIFEST.MF
|--WEB-INF/
|--web.xml
|--lib/
- .settings为Eclipse项目文件夹,存放了Eslipse项目的各种配置。在Eclipse项目视图中不可见。
- src目录存放源码。在Eclipse的项目视图中对应为Java Resources/src。
- build存放编译后的文件。
- 可以在类似的\workspace\.metadata\.plugins\org.eclipse.wst.server.core\tmp1\wtpwebapps\DynamicWP目录中查看运行时的文件结构。
3.Maven Web项目的基本结构
鉴于目前Java IDE众多并且都有一定的拥泵,Eclipse的Java Web项目不具有可移植性。Maven即解决了项目结构的规范问题又提供了强大引用处理等强大的功能,在项目布局等方面已经是目前事实上的标准。Maven项目的主要结构如下(参考2):
|--root |--pom.xml |--src/ |--main/ |--java/ |--resources/ |--webapp/ |--test/ |--java/ |--resources |--target/
Eclipse中新建一个Maven web app项目。文件结构如下:
|--MavenWP
|--pom.xml
|--.project
|--.classpath
|--.settings/
|--src/
|--target/
|--classes/
|--m2e-wtp/
- pom.xml:maven项目配置文件。
- .project文件和.classpath文件以及.settings目录和target/m2e-wtp目录下的文件为Eclipse项目配置文件。
- src和target:maven标准项目目录。
Eclipse4.5.1中对应的项目资源管理视图
|--MavenWP |--Deployment Desciptor/ |--Java Resources/ |--JavaScript Resources/ |--Deployed Resources/ |--src |--target |--pom.xml
- 默认创建的项目会添加一个index.jsp并报错:使用maven搜索并添加servlet依赖更新后就可以正常运行。
- Java构建路径问题警告:使用maven搜索并添加compiler插件并配置configuration节点更新就可以消除。
- 墙的问题配置maven镜像,我采用的是http://maven.oschina.net/content/groups/public/。
- 默认创建的maven webapp缺少的src/main/java、src/test/java和src/test/resources等目录需要自己手动添加。
- 修改.settings/org.eclipse.wst.common.project.facet.core.xml,更新<installed facet="jst.web" version="3.1"/>。
- web.xml根节点开始部分修改如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" version="3.1">
Maven的配置文件pom.xml:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>me.test</groupId> <artifactId>MavenWP</artifactId> <packaging>war</packaging> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>MavenWP Maven Webapp</name> <url>http://maven.apache.org</url> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>3.8.1</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>3.1.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <finalName>MavenWP</finalName> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.3</version> <configuration> <source>1.8</source> <target>1.8</target> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
4.servlet基础
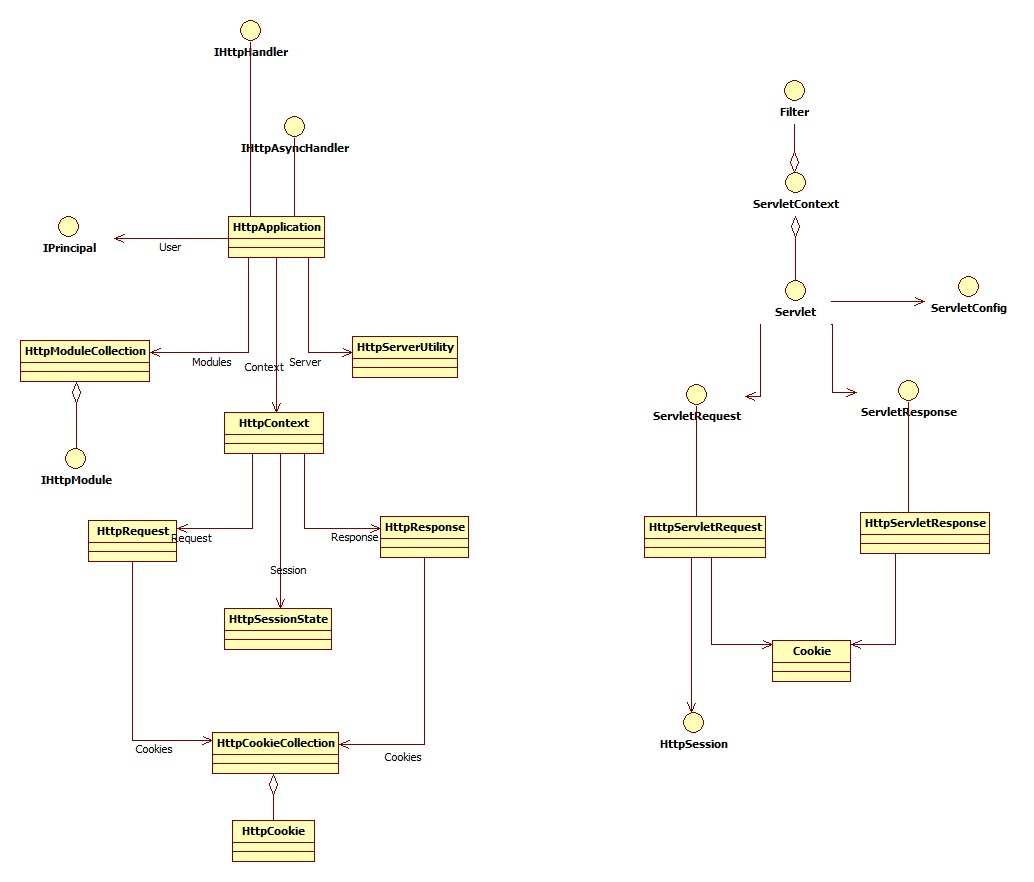
正如ASP.NET的核心是IHttpHandler一样,Java Web的核心是Servlet接口,位于javax.servlet命名空间中。Filter的概念可以参考ASP.NET的HttpModule,Servlet中的各种Listener可以参考ASP.NET HttpApplicaiton中类似的event。无论是Java还是.NET的Web技术,都是基于HTTP协议的具体实现。Java Web和ASP.NET中的一些核心项对应如下:
| Java 参考3 | .NET | 备注 | |
| Core | javax.servlet.Servlet | System.Web.IHttpHandler | |
| HTTP Request | javax.servlet.ServletRequest | System.Web.HttpRequest | |
| HTTP Response | javax.servlet.ServletResponse | System.web.HttpResponse | |
| Cookie | javax.servlet.http.Cookie | System.Web.HttpCookie | |
| Session | javax.servlet.http.HttpSession | System.Web.HttpSessionState | |
| Application | javax.servlet.ServletContext | System.Web.HttpApplication | |
| Begin Request | javax.servlet.Servlet.RequestDispatcher | System.Web.HttpApplication.BeginRequest | event |
| Begin\End Request | javax.servlet.Servlet.ServletRequestListener | System.Web.HttpApplication.BeginRequest\EndRequest | event |
| Filter | javax.servlet.Filter | System.Web.IHttpModule | |
| Application Event | javax.servlet.ServletContextListener | System.Web.HttpApplication.Application_Start\Application_End | method |
Servlet和ASP.NET的简化示意图:
用于简化web.xml配置的Servlet的注解(3.0开始支持,在ASP.NET中没有对应项):
(1)WebServlet:作用在javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet的实现类上。
(2)WebFilter:作用在javax.servlet.Filter的实现类上。
(3)WebListener:作用在Listener的实现类上(javax.servlet.ServletContextListener、javax.servlet.ServletContextAttributeListener、javax.servlet.ServletRequestListener、javax.servlet.ServletRequestAttributeListener、javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionListener、javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionAttributeListener)。
(4)WebInitParam:结合WebServlet和WebFilter注解用来配置属性。
(5)MultipartConfig:作用在javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet的实现类上。标注请求是mime/multipart类型。
用于Servlet容器初始化的ServletContainerInitializer(可实现无web.xml,3.0开始支持,可类比ASP.NET的Application_Start方法):
(1)Servlet容器启动时查找ServletContainerInitializer的实例。
(2)ServletContainerInitializer实例使用HandlesTypes标注一个或多个类型,Servlet容器将在启动时扫描classpath,获取这些类型的实例。
(3)Servlet容器在启动时调用ServletContainerInitializer实现类的onStartup方法,该方法可以获取HandlesTypes标注的所有类型对象。
5.自定义Session
Session在存储安全性要求较高的会话信息方面是必不可少的,Session当然绝对不是用来存储用户登录状态的,但类似验证码等敏感信息却必须存储在Session中。对于分布式Web应用自定义Session支持独立的状态服务器或集群是必须的。
ASP.NET通过SessionStateModule通过配置文件配置实际的Session提供程序,Session提供程序实现了SessionStateStoreProviderBase,因此在ASP.NET中实现自定义Session是通过继承SessionStateStoreProviderBase实现,配置Session是通过Web.config。ASP.NET自定义session的代码参考github上的开源项目SQLiteSessionStateStore。
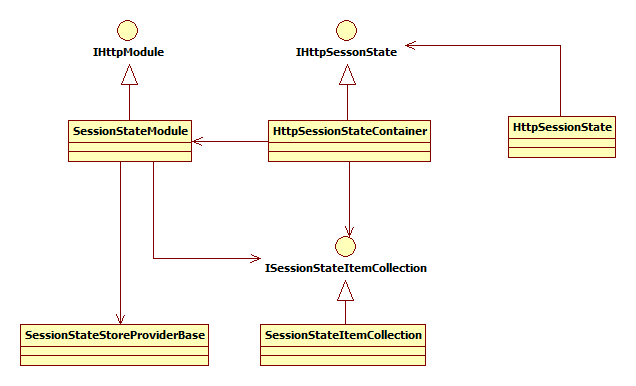
同理,Java Servlet中使用自定义Session通过Filter可以实现。由于不同的servlet容器对Session的实现不同,所以通用性最好的方式是继承HttpServletRequestWrapper重写getSession方法返回自定义的Session对象。Filter采用了职责链模式(chain of responsibility),HttpServletRequestWrapper采用了装饰模式(Decorator),可以通过《Head First 设计模式》阅读模式的相关内容。
(1)首先自定义继承HttpSession的MySession(为了便于演示,仅包装了容器的session并转发调用)。

import java.util.Enumeration; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession; public class MySession implements HttpSession { private HttpSession _containerSession; public MySession(HttpSession session) { this._containerSession = session; } @Override public long getCreationTime() { return this._containerSession.getCreationTime(); } @Override public String getId() { return this._containerSession.getId(); } @Override public long getLastAccessedTime() { return this._containerSession.getLastAccessedTime(); } @Override public ServletContext getServletContext() { return this._containerSession.getServletContext(); } @Override public void setMaxInactiveInterval(int interval) { this._containerSession.setMaxInactiveInterval(interval); } @Override public int getMaxInactiveInterval() { return this._containerSession.getMaxInactiveInterval(); } @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") @Override public HttpSessionContext getSessionContext() { return this._containerSession.getSessionContext(); } @Override public Object getAttribute(String name) { return this._containerSession.getAttribute(name); } @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") @Override public Object getValue(String name) { return this._containerSession.getValue(name); } @Override public Enumeration<String> getAttributeNames() { return this._containerSession.getAttributeNames(); } @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") @Override public String[] getValueNames() { return this._containerSession.getValueNames(); } @Override public void setAttribute(String name, Object value) { this._containerSession.setAttribute(name, value); } @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") @Override public void putValue(String name, Object value) { this._containerSession.putValue(name, value); } @Override public void removeAttribute(String name) { this._containerSession.removeAttribute(name); } @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") @Override public void removeValue(String name) { this._containerSession.removeValue(name); } @Override public void invalidate() { this._containerSession.invalidate(); } @Override public boolean isNew() { return this._containerSession.isNew(); } }
(2)自定义继承HttpServletRequestWrapper的MyRequest

import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequestWrapper; import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession; public class MyRequest extends HttpServletRequestWrapper { public MyRequest() { super(null); } public MyRequest(HttpServletRequest request) { super(request); // TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根 } @Override public HttpSession getSession(boolean create) { return new MySession(super.getSession(create)); } @Override public HttpSession getSession() { return new MySession(super.getSession()); } }
(3)自定义Filter将Request包装为MyRequest

import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.Filter; import javax.servlet.FilterChain; import javax.servlet.FilterConfig; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.ServletRequest; import javax.servlet.ServletResponse; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; @WebFilter("/*") public class MyFilter implements Filter { @Override public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 } @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { chain.doFilter(new MyRequest((HttpServletRequest) request), response); } @Override public void destroy() { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 } }
通过注解配置了Filter,也可以通过原始的web.xml方式配置。
6.参考
1.https://docs.oracle.com/javaee/7/tutorial/packaging003.htm
2.http://maven.apache.org/guides/introduction/introduction-to-the-standard-directory-layout.html
3.https://docs.oracle.com/javaee/7/tutorial/webapp005.htm
小结:
你至少应该知道的:
(1)配置文件:ASP.NET的web.config和Java的web.xml
(2)Web核心:ASP.NET的IHttpHandler接口和Java的Servlet接口
(3)拦截器:ASP.NET的HttpModule和Java的Filter
(4)应用程序事件:ASP.NET的HttpApplication event和Java的各种Listener
(5)启动器:ASP.NET的Application_Start和Java的ServletContainerInitializer
(6)引用管理:ASP.NET的Nuget和Java的Maven
感想:
ASP.NET的核心对象不像Java Servlet一样,从一开始就基于接口,这是缺点。但Java Servlet的核心对象全靠容器实现,就连HttpSession同样如此,这也是缺点。比如自定义个Session十分麻烦,没有像ASP.NET一样简单配置即可。另外Servlet的一些抽象定义有点过头了,不够简洁。



发表评论 取消回复