Spring浅入浅出——不吹牛逼不装逼
前言:
今天决定要开始总结框架了,虽然以前总结过两篇,但是思维是变化的,而且也没有什么规定说总结过的东西就不能再总结了,是吧。这次总结我命名为浅入浅出,主要在于理解框架核心,轻松愉快使用框架。
核心思想
我们都学了面向对象,在生活中,当人们需要一件东西时,第一反应就是找东西,例如想吃面包,现在有两种情况,第一种是没有面包店,第二种是有面包店。第一种情况就是我们之前一直遇到的情况,在没有面包店的情况下,最直观的做法可能就是你按照自己的口味制作面包,也就是一个面包需要主动制作,谁想吃了就自己New。而我主要说的是第二种情况,就是有面包店,你想吃面包的时候找到面包店,把自己的口味告诉店家,店家就可以给你做符合你口味的面包了。注意:你并没有制作面包,而是由店家制作,但是完全符合你的口味。
这是一个很生活的例子,大家都明白,但这里包含了Spring中很重要的思想——控制反转,就是把制作面包的主动权交给店家,面包就是对象,店家相当于一个大容器,你想要什么对象,就让大容器去给你生产,这就是控制反转思想。
再详细点,当某个Java对象(调用者,例如你)需要调用另一个Java对象(被调用者,即被依赖对象,例如面包)时,在传统编程模式下,调用者通常会采用“New 被调用者”的代码方式来创建对象(例如你自己制作面包)。这种方式会增加调用者与被调用者之间的耦合性,不利于后期代码的升级和维护。
当Spring框架出现后,对象的实例不再由调用者来创建,而是由 Spring容器(例如面包店)来创建。Spring容器会负责控制程序之间的关系(例如面包店负责控制你与面包的关系),而不是由调用者的程序代码直接控制。这样,控制权由调用者转移到Spring容器,控制权发生了反转,这就是Spring的控制反转。
在之前,我们需要用构造方法或者set()方法给一些成员变量赋值,从Spring容器角度来看,Spring容器负责将被依赖对象赋值给调用者的成员变量,相当于为调用者注入它所依赖的实例,这就是Spring的依赖注入。
综上所述,控制反转是一种通过描述(在Spring中可以是XML或注解)并通过第三方去产生或获取特定对象的方式。在Spring中实现控制反转的是IoC容器,其实现方法是依赖注入。
Spring IoC容器
看完上面所述,我们知道实现控制反转的是Spring IoC容器。Spring IoC容器的设计主要是基于BeanFactory和ApplicationContext两个接口。
先说BeanFactory,它提供了完整的IoC服务支持,是一个管理Bean的工厂,主要负责初始化各种Bean。BeanFactory接口有多个实现类,其中比较常用的是org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory,该类会根据XML配置文件中的定义来装配Bean.由于BeanFactory实例加载Spring配置文件在实际开发中并不多见,只需了解即可,我也不过多解说了。
再说ApplicationContext,它是BeanFactory的子接口,也称为应用上下文,ApplicationContext接口除了包含BeanFactory的所有功能以外,还添加了对国际化、资源访问、事件传播等内容的支持。创建ApplicationContext接口实例通常有三种方法:
1、 通过ClassPathXmlApplicationContext创建
2、 通过FileSystemXmlApplicatonContext创建
3、 通过Web服务器实例化ApplicationContext容器
作为一个初学者,我觉得先会用第一种就可以了,所以我主要解说第一种,别的等你自己入门后自己看,我只做引导。
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext将从类路径目录(src根目录)中寻找指定的XML配置文件,如下代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //初始化SPring容器,加载配置文件 ApplicationContext appCon = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml"); //通过容器获得test实例 TestDao tt = (TestDao) appCon.getBean("test"); tt.sayHello(); }} |
依赖注入的类型
在Spring中实现IoC容器的方法是依赖注入,依赖注入的作用是在使用Spring框架创建对象时动态地将其所依赖的对象(例如属性值)注入Bean组件中,Spring框架的依赖注入通常有两种实现方式,一种是使用构造方法注入,另一种是使用属性的setter方法注入。具体且看实例演示
实例演示
一、在pom.xml中导入相应模块
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 | <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.11</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>3.1.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>jstl</artifactId> <version>1.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>commons-logging</groupId> <artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId> <version>1.2</version> </dependency> <!--spring核心依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.38</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId> <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId> <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId> <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-web</artifactId> <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-expression</artifactId> <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId> <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version> </dependency></dependencies> |
二、创建TestDao
1 2 3 4 5 | package com.my.dao;public interface TestDao { public void sayHello();} |
三、创建TestDaoImpl
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | package com.my.dao.impl;import com.my.dao.TestDao;public class TestDaoImpl implements TestDao { @Override public void sayHello() { System.out.println("Hello Spring!!!"); }} |
四、创建spring-config.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd "> <bean id="testDIDao" class="com.my.dao.impl.TestDaoImpl"/></beans> |
五、测试Test
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | package com.my.test;import com.my.dao.TestDao;import com.my.dao.impl.TestDaoImpl;import com.my.service.TestService;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //调用者自己创建对象 TestDao testDao = new TestDaoImpl(); testDao.sayHello(); //初始化SPring容器,加载配置文件 ApplicationContext appCon = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml"); //通过容器获得test实例 TestDao tt = (TestDao) appCon.getBean("testDIDao"); tt.sayHello(); }} |
六、测试结果
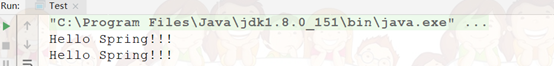
七、创建TestService
1 2 3 4 5 | package com.my.service;public interface TestService { public void sayHello();} |
八、创建TestServiceImpl
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | package com.my.service.impl;import com.my.dao.TestDao;import com.my.service.TestService;public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService { private TestDao testDao;//构造方法,用于实现依赖注入接口对象TestDao public TestServiceImpl(TestDao testDao) { this.testDao = testDao; } @Override public void sayHello() { testDao.sayHello(); }} |
九、在spring-config.xml中注入
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd "> <!--将指定类TestDaoImpl配置给Spring,让Spring创建其实例--> <bean id="testDIDao" class="com.my.dao.impl.TestDaoImpl"/> <!--使用构造方法注入--> <bean id="testDIService" class="com.my.service.impl.TestServiceImpl" > <!--将TestDIDao注入到TestDIServiceImpl类的属性testDao上--> <constructor-arg index="0" ref="testDIDao"/> </bean></beans> |
十、测试Test
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | package com.my.test;import com.my.dao.TestDao;import com.my.dao.impl.TestDaoImpl;import com.my.service.TestService;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //调用者自己创建对象 TestDao testDao = new TestDaoImpl(); testDao.sayHello(); //初始化SPring容器,加载配置文件 ApplicationContext appCon = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml"); //通过容器获得test实例 TestDao tt = (TestDao) appCon.getBean("testDIDao"); tt.sayHello(); //通过容器获取TestService实例,测试构造方法注入 TestService testService =(TestService) appCon.getBean("testDIService"); testService.sayHello(); }} |
十一、测试结果
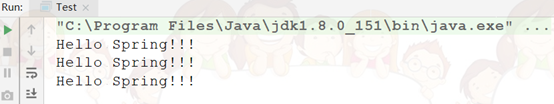
十二、使用属性的setter方法注入
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | package com.my.service.impl;import com.my.dao.TestDao;import com.my.service.TestService;public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService { private TestDao testDao; //添加testDao属性的setter方法,用于实现依赖注入 public void setTestDao(TestDao testDao){ this.testDao=testDao; } @Override public void sayHello() { testDao.sayHello(); }} |
十三、在spring-config.xml中注入
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd "> <!--将指定类TestDaoImpl配置给Spring,让Spring创建其实例--> <bean id="testDIDao" class="com.my.dao.impl.TestDaoImpl"/> <!--使用setter方法注入--> <bean id="testDIService" class="com.my.service.impl.TestServiceImpl"> <!--调用TestDIServiceImpl类的setter方法,将TestDao注入到TestServiceImpl类的属性testDao上--> <property name="testDao" ref="testDIDao"></property> </bean></beans> |
十四、测试Test
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | package com.my.test;import com.my.dao.TestDao;import com.my.dao.impl.TestDaoImpl;import com.my.service.TestService;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //调用者自己创建对象 TestDao testDao = new TestDaoImpl(); testDao.sayHello(); //初始化SPring容器,加载配置文件 ApplicationContext appCon = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml"); //通过容器获得test实例 TestDao tt = (TestDao) appCon.getBean("testDIDao"); tt.sayHello(); //通过容器获取TestService实例,测试setter方法注入 TestService testService =(TestService) appCon.getBean("testDIService"); testService.sayHello(); }} |
十五、测试结果

注入说明
在Src根目录下创建Spring配置文件spring-config.xml(文件名随意,注意后缀.xml)。在配置文件中,constructor-arg元素用于定义类构造方法的参数,index用于定义参数的位置,ref指定某个实例的引用,如果参数是常量值,ref由value代替。
特别链接
看完此篇后你觉得理解了,可以看看我以前写的这几篇博客,会有帮助的
《没有无缘无故的编程》https://www.cnblogs.com/zyx110/p/11297822.html
《路过别错过》https://www.cnblogs.com/zyx110/p/11271820.html
《spring框架知多少》https://www.cnblogs.com/zyx110/p/11022891.html
《用IDEA开发Spring程序》https://www.cnblogs.com/zyx110/p/11023218.html
结束语
此篇Spring浅入浅出到此结束,作此篇是为了让初学者放下心理枷锁,先理解,其实挺好理解的,等你有信心后自己学习就可以了,希望能对一些朋友有所帮助,加油。
*****************************************************************************************************
我的博客园地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zyx110/
本文已独家授权给脚本之家(jb51net)公众号独家发布

发表评论 取消回复