@ResponseStatus这个注解确实是个令我头疼的注解.
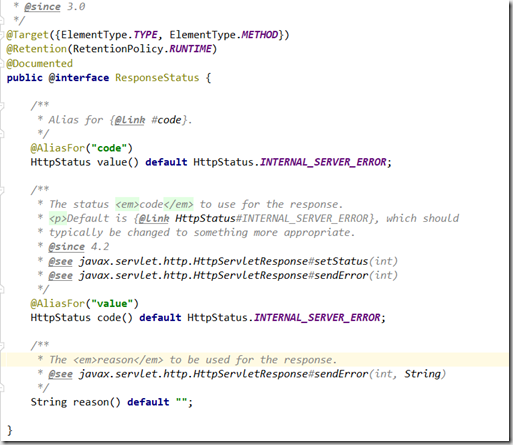
先记录下@ResponseStatus注解的定义. 记录几个得到的信息:@ResponseStatus声明在方法、类上, Spring3.0开始才有的, 三个属性其中 HttpStatus类型的 value 和 code是一个含义, 默认值就是 服务器 500错误的 HttpStatus.
用法一.标注在@RequestMapping方法上.
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 | @Controller@RequestMapping("/simple")public class SimpleController { @RequestMapping("/demo2") @ResponseBody @ResponseStatus(code = HttpStatus.OK) public String demo2(){ return "hello world"; }} |
上面说了 code 和 value一个意思,这里我就用code了,相对而言比较喜欢code单词. 这里作用就是改变服务器响应的状态码 ,比如一个本是200的请求可以通过@ResponseStatus 改成404/500等等.
常见的几个状态码 HttpStatus.OK 就是 200 , HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR 就是 500 等等 ,具体的查看 HttpStatus枚举 有详细说明.
实现原理呢,注解底层还是通过设置 response.setStatus来实现.
在@RequestMapping方法执行完成,Spring解析返回值之前,进行了responseStatus设置.
代码片段位于:org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ServletInvocableHandlerMethod#setResponseStatus
this对象指当前的ServletInvocableHandlerMethod,看到 @ResponseStatus的reason不为空,就调用response.sendError ; reason为空,就调用setStatus方法仅仅设置响应状态码.
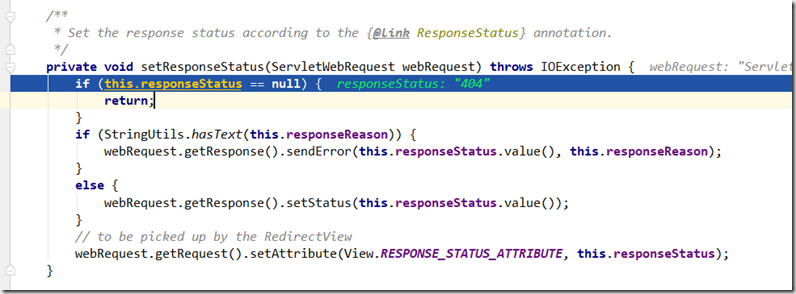
记录下在哪里调用了这个responseStatus方法?
代码片段位于:org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ServletInvocableHandlerMethod#invokeAndHandle
发现如果ServletInvocableHandlerMethod的responseReason有值,也就是@ResponseStatus有reason属性,@RequestMapping方法返回值都不处理了,直接返回;
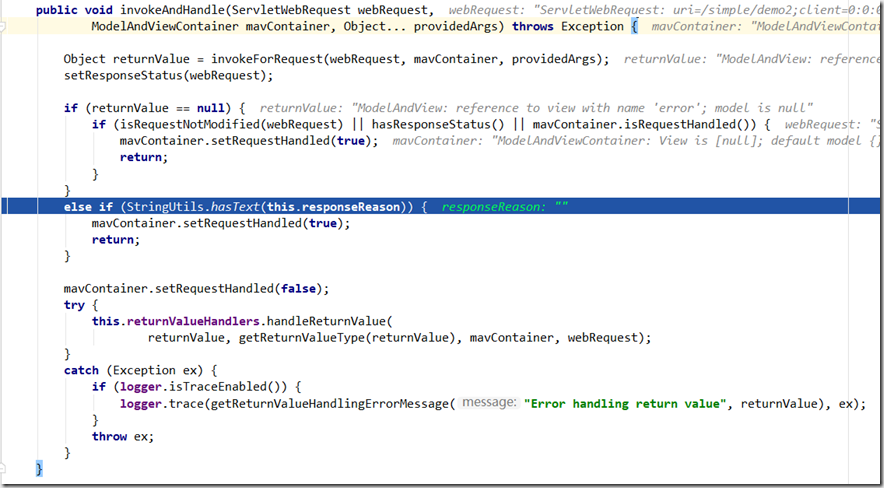
也就是说只要有@ResponseStatus的 reason属性标注在 处理器Controller类或者方法上,比如响应状态码code设置为 404,reason设置为页面没找到 ,那 tomcat 展示界面是这样大概,展示信息就是我们写的reason属性.
@ResponseStatus(code=A,reason=B)标注在 @RequestMapping方法上,作用效果与 response.sendError(A,B)是一样的.
所以,@ResponseStatus我建议啊, 这种方式下使用千万不要加 reason, 就把@ResponseStatus 当做一个用来改变响应状态码的方式!
用法二.标注在@ControllerAdvice中.
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 | @ControllerAdvice@ResponseStatuspublic class MyControllerAdvice { @ExceptionHandler({ArithmeticException.class}) public ModelAndView fix(Exception e){ Map map=new HashMap(); map.put("ex",e.getMessage()); return new ModelAndView("error",map); }} |
@ControllerAdvice标注初衷我想就是程序运行过程中发生异常,对异常如何处理? 而@ResponseStatus标注在@ControllerAdvice类或者该类下的@ExceptionHandler上,区别大概就是,
原来比如请求程序抛出异常,异常被捕获,走@ExceptionHandler,正常走完状态码是200.
@ControllerAdvice或者 @ExceptionHandler标注了@ReponseStatus,那走完状态码就是500.
如果你再给@ResponseStatus添加了reason属性,不管捕获异常方法咋返回,都是服务器的错误码捕获界面,比如上面我的例子,给@ResponseStatus添加reason=”your defined message”.
不管怎么说,下面界面比一大堆异常堆栈信息看起来更简洁,但我还是不推荐使用诶,原因啊,界面不友好.
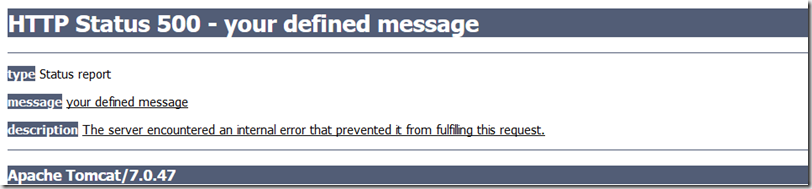
用法三.自定义类型的异常添加注解@ResponseStatus
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 | @ResponseStatus(code = HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR,reason = "not an error , just info")public class MyException extends RuntimeException { public MyException() { } public MyException(String message) { super(message); }} |
这样子,在SpringMvc中如果有某个 @RequestMapping方法抛出该异常, 只要开启<mvc:annotation-driven/>,异常自动展示的界面都是如下的:
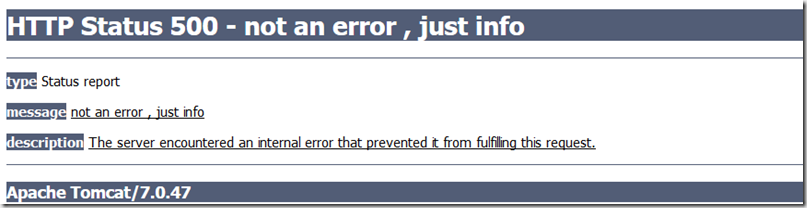
SpringMvc异常捕获方法如下.
代码片段位于:org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#processHandlerException
<mvc:annotation-driven/>注册了三个HandlerExceptionResolver:ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver用来处理@ExceptionHandler,而ResponseStatusExceptionResolver是用来处理抛出的异常上标注了@ResponseStatus的解析器.
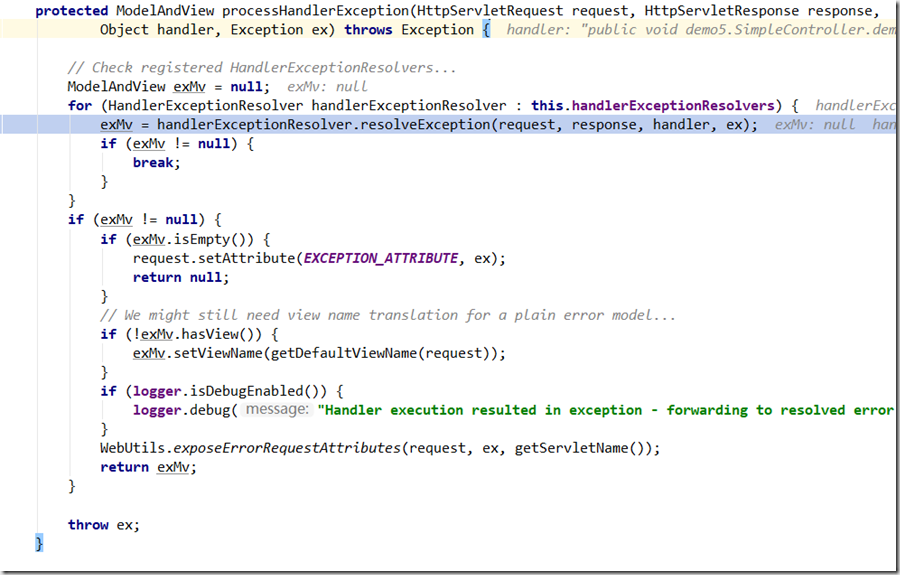
ResponseStatusExceptionResolver解析异常方式:
代码片段位于:org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver#doResolveException
ex就是@RequestMapping方法抛出自定义的异常,使用工具类解析自定义异常上的@ResponseStatus注解,找到注解就调用resolveResponseStatus进行响应的处理。
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | protected ModelAndView doResolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) { ResponseStatus responseStatus = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(ex.getClass(), ResponseStatus.class); if (responseStatus != null) { try { return resolveResponseStatus(responseStatus, request, response, handler, ex); } catch (Exception resolveEx) { logger.warn("Handling of @ResponseStatus resulted in Exception", resolveEx); } } else if (ex.getCause() instanceof Exception) { ex = (Exception) ex.getCause(); return doResolveException(request, response, handler, ex); } return null; } |
ResponseStatusExceptionResolver如何根据异常上的@ResponseStatus处理响应?
代码片段位于:org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver#resolveResponseStatus
获取了@ReponseStatus的 code reason属性,reason不为空就 response.sendError(statusCode, reason) ,并且返回一个空的ModelAndView,这里的ModelAndView已经没有意义了,SendError方法简单来说就是会跳转到web.xml中配置的 错误状态码 对应的页面, 没有配置就是默认的服务器的那种错误界面,且只展示 前面的reason信息,即响应类型为text/html .
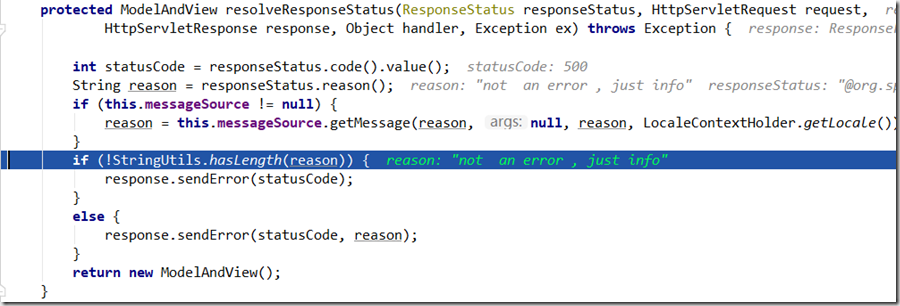
总结:
不管哪种方式,@ReponseStatus最后都是通过response.setStatus或response.sendError来处理.
如果只是为了返回状态码,建议只使用 @ResponseStatus(code=xxxx)这样来设置响应状态码;
如果抛出异常呢,不建议@ControllerAdvice里面的 @ResponseStatus和 自定义异常上的 @ResponseStatus一起使用, 按照我的阅读理解,两个一起使用肯定是一个生效,而且是 @ControllerAdvice中的@ResponseStatus生效.
场景分析:假设抛出异常不是我们自定义的异常,我们想改变响应的状态码,通过@ExceptionHandler来处理异常,并在@ExceptionHandler方法上也可以设置@ResponseStatus来达到效果;
假如抛出自定义的异常,自己没有定义异常处理界面,那在异常上标注@ResponseStatus就可以走 服务器默认的界面展示,或者通过web.xml 配置error-code \ error-page来自定义界面处理异常;

发表评论 取消回复